I have been explaining the broad and narrow folksonomy in e-mail and in comments on others sites, as well as in the media (Wired News). There has still been some confusion, which is very understandable as it is a different concept that goes beyond a simple understanding of tagging. I have put together a couple graphics that should help provide a means to make this distinction some what clearer. The folksonomy is a means for people to tag objects (web pages, photos, videos, podcasts, etc., essentially anything that is internet addressable) using their own vocabulary so that it is easy for them to refind that information again. The folksonomy is most often also social so that others that use the same vocabulary will be able to find the object as well. It is important to note that folksonomies work best when the tags used to describe objects are in the common vocabulary and not what a person perceives others will call it (the tool works like no other for personal information management of information on the web, but is also shared with the world to help others find the information).
Broad Folksonomy
Let's begin with the broad folksonomy, as a tool like del.icio.us delivers. The broad folksonomy has many people tagging the same object and every person can tag the object with their own tags in their own vocabulary. This lends itself very easy to applying the power law curve (power curve) and/or net effect to the results of many people tagging. The power terms and the long tail both work.
The broad folksonomy is illustrated as follows.
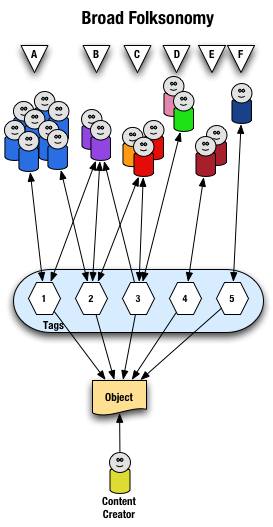
From a high level we see a person creates the object (content) and makes it accessible to others. Other people (groups of people with the same vocabulary represented people blobs and noted with alphabet letters) tag the object (lines with arrows pointing away from the people) with their own terms (represented by numbers). The people also find the information (arrows on lines pointing from the numeric tags back to the people blobs) based on the tags.
Digging a little deeper we see quite a few people (8 people) in group "A" and they have tagged the object with a "1" and a "2" and they use this term to find the object again. Group "B" (2 people) have applied tag "1" and "2" to the object and they use tag terms "1", "2", and "3" to find the information. Group "C" (3 people) have tagged the object with "2" and "3" so that they can find the object. Group "D" has also tagged the object with tag "3" so that they may refind the information this group may have benefitted from the tagging that group "C" provided to help them find the information in the first place. Group "E" (2 people) uses a different term, "4", to tag the object than others before it and uses only this term to find the object. Lastly, group "F" (1 person) uses tag "5" on the object so that they may find it.
Broad Folksonomy and the Power Curve
The broad folksonomy provides a means to see trends in how a broad range are tagging one object. This is an opportunity to see the power law curve at work and show the long-tail.
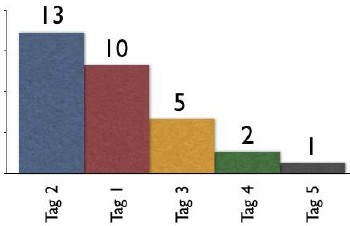
The tags spike with tag "2" getting the largest portion of the tags with 13 entries and tag "1" receiving 10 identical tags. From this point the trends for popular tags are easy to see with the spikes on the left that there are some trends, based on only those that have tagged this object, that could be used extract a controlled vocabulary or at least know what to call the object to have a broad spectrum of people (similar to those that tagged the object, and keep in mind those that tag may not be representative of the whole). We also see those tags out at the right end of the curve, known as the long tail. This is where there is a small minority of people who call the object by a term, but those people tagging this object would allow others with a similar vocabulary mindset to find the object, even if they do not use the terms used by the masses over at the left end of the curve. If we take this example and spread it out over 400 or 1,000 people tagging the same object we will se a similar distribution with even more pronounced spikes and drop-off and a longer tail.
This long tail and power curve are benefits of the broad folksonomy. As we will see the narrow folksonomy does not have the same properties, but it will have benefits. These benefits are non-existent for those just simply tagging items, most often done by the content creator for their own content, as is the means Technorati has done, even with their following tag links to destinations other than Technorati (as they initially had laid out). The benefits of the long tail and power curve come from the richness provided by many people openly tagging the same object.
Narrow Folksonomy
The narrow folksonomy, which a tool like Flickr represents, provides benefit in tagging objects that are not easily searchable or have no other means of using text to describe or find the object. The narrow folksonomy is done by one or a few people providing tags that the person uses to get back to that information. The tags, unlike in the broad folksonomy, are singular in nature (only one tag with the term is used as compared to 13 people in the broad folksonomy using the same tag). Often in the narrow folksonomy the person creating the object is providing one or more of the tags to get things started. The goals and uses of the narrow folksonomy are different than the broad, but still very helpful as more than one person can describe the one object. In the narrow the tags are directly associated with the object. Also with the narrow there is little way of really knowing how the tags are consumed or what portion of the people using the object would call it what, therefore it is not quite as helpful as finding emerging vocabulary or emergent descriptions. We do find that tags used to describe are also used for grouping, which is particularly visible and relevant in Flickr (this is also done in broad folksonomies, but currently not to the degree of visibility that it is done on Flickr, which may be part of the killer interactive environment Ludicorp has created for Flickr).
The narrow folksonomy is illustrated as follows.
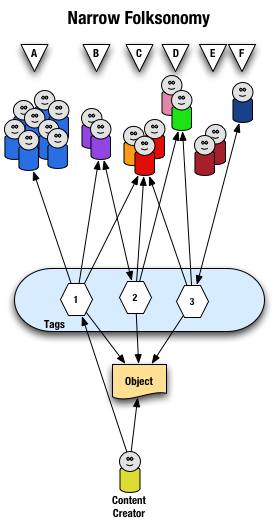
From a high level we see a person creates the object and applies a tag ("1") that represents what they call the object or believe describes the object. There are fewer tags provided than in a broad folksonomy and there is only one of each tag applied to the object. The consumers of the object also can apply tags that help them find the object or describe what they believe are the terms used to describe this object.
A closer look at the interaction between people and the object and tags in a narrow folksonomy shows us that group "A" uses tag "1" to find and come back to the object (did the creator do this on purpose? or did she just tag it with what was helpful to her). We see group "B" also using tag "1" to find the object, but they have tagged the object with tag "2" to also use as a means to find the object. Group "C" uses tag "1","2", and "3" to find the object and we also note this group did not apply any of its own tags to the object as so is only a consumer of the existing folksonomy. We see group "D" uses tags "2" and "3" to find the objects and it too does not add any tags. Group "E" is not able to find the object by using tags as the vocabulary it is using does not match any of the tags currently provided. Lastly, group "F" has their own tag for the object that they alone use to get back to the object. Group "F" did not find the object through existing tags, but may have found the object through other means, like a friend e-mailed them a link or the object was included in a group they subscribe to in their feed aggregator.
We see that the richness of the broad folksonomy is not quite there in a narrow folksonomy, but the folksonomy does add quite a bit of value. The value, as in the case of Flickr, is in text tags being applied to objects that were not findable using search or other text related tools that comprise much of how we find things on the internet today. The narrow folksonomy does provide various audiences the means to add tags in their own vocabulary that will help them and those like them to find the objects at a later time. We are much better off with folksonomies than we were with out them, even if it is a narrow folksonomy being used.
Conclusion
We benefit from folksonomies as the both the personal vocabulary and the social aspects help people to find and retain a tether to objects on the web that are an interest to them. Who is doing the tagging is important to understand and how the tags are consumed is an important factor. This also helps us see that not all tagging is a folksonomy, but is just tagging. Tagging in and of its self is a helpful step up from no tagging, but is no where near as beneficial as opening the tagging to all. Folksonomy tagging can provide connections across cultures and disciplines (an knowledge management consultant can find valuable information from an information architect because one object is tagged by both communities using their own differing terms of practice). Folksonomy tagging also makes up for missing terms in a site's own categorization system/taxonomy. This hopefully has made things a little clearer for all in our understanding the types of folksonomies and tagging and the benefits that can be derived.
This entry first appeared at Personal InfoCloud and comments are open for your use there.


